Hallmarks and purity of metals
Purity indicates the relative weight content of pure precious metal in the alloy, and every investor or collector is justifiably interested in whether its gold is pure. But how to easily recognize the purity of gold?
The purity of gold, but also the purity of silver and platinum is expressed in several ways, and in the case of commemorative medals, it can be determined at first glance - the legal hallmarks are used to indicate purity. It can be more difficult to recognize the purity of a coin or ingot - they do not bear the hallmark, but usually the indication of purity is embossed on them in another way, for example in the form of a purity number. Products of solid manufacturers always includes a certificate of origin and authenticity, which, in addition to other specifications, also states the purity of the precious metal used.
Purity can also be expressed in carats, but it is more common in the field of jewelry. Pure metal (999/1000) has a 24 carat marking in this system, an alloy with half the gold content (500/1000) is then marked with a half value as 12 carats.
|
Percentage of pure metal |
Fineness number
|
Purity in carats |
|
99.99% |
999.9
|
24
|
|
91.66% |
916.6
|
22
|
|
75.00% |
750
|
18
|
|
58.33% |
585
|
14
|
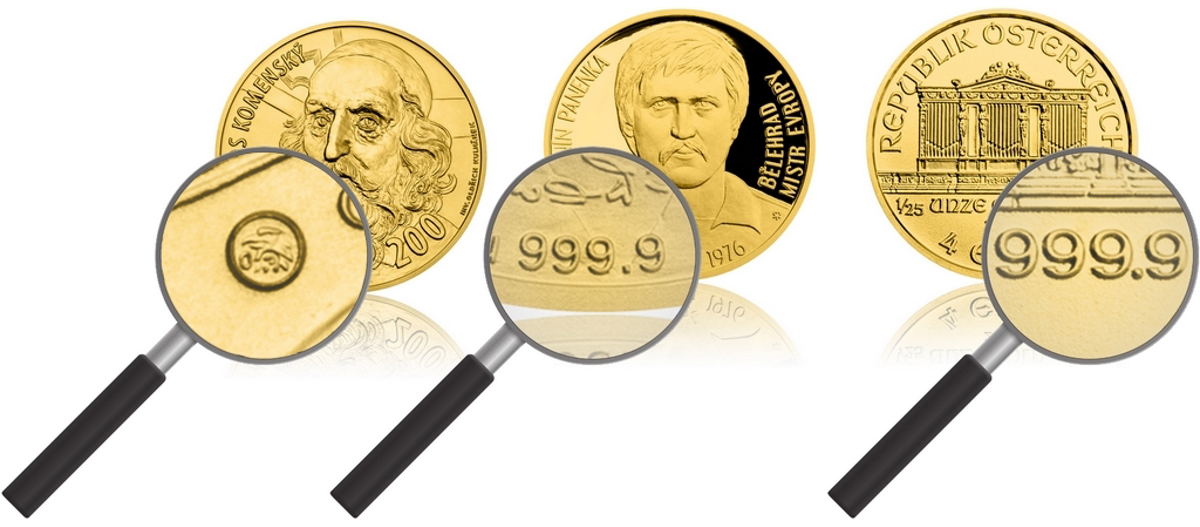

hallmark on the gold medal of the Czech Mint / fineness number on the gold Smart coin of the Czech Mint / fineness number on the gold coin of the Austrian Mint
Marking products with hallmarks is governed by Act No. 539/1992 Coll. of hallmarking and testing of precious metals (Hallmarking Act). Products are marked for labeling by the manufacturer or trader.
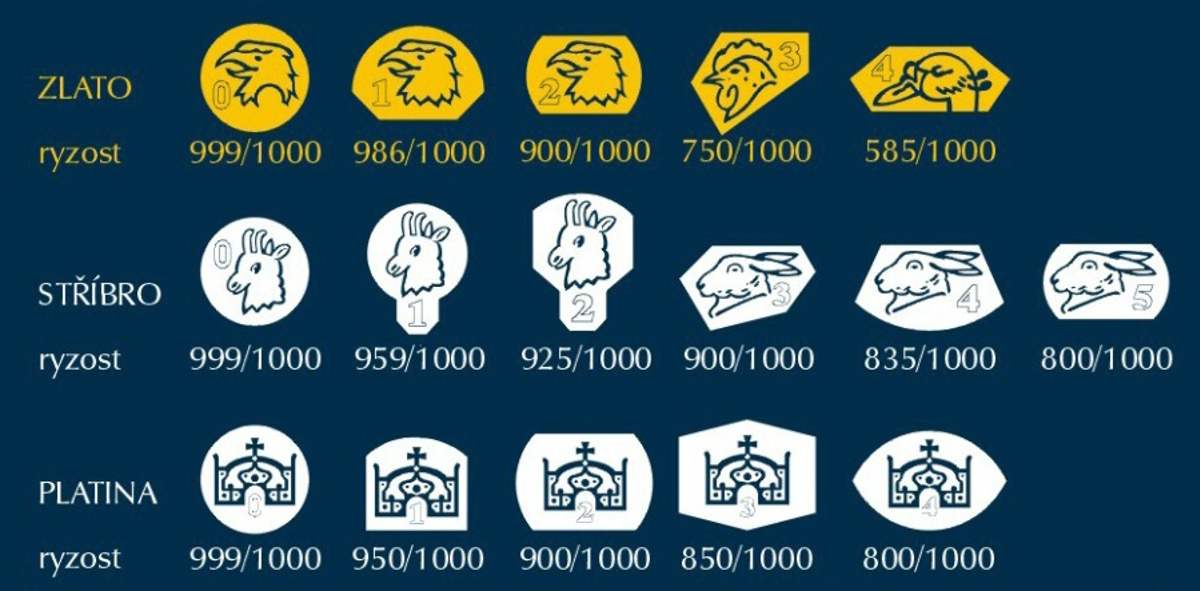
currently used Czech hallmarks
The mark is placed on the stamping dice of the Czech Mint by the Assay Office in Jablonec nad Nisou, which also carries out a continuous inspection of the purity of its cuts. The hallmarks contain the distinction of individual workplaces of the Assay Office in the form of miniature letters, which are oriented perpendicular to the vertical axis of the mark.

hallmark of the Assay Office in Jablonec nad Nisou contains the letter "J"
Coins are not marked with hallmarks (Czech or foreign), nor ingots they are not goods(in the sense of the Punching Act) - these usually contain information on purity given in numerical form.
In an effort to facilitate international trade in goods made of precious metals, the Convention on the Control and Marking of Articles of Precious Metals was adopted - the so-called Convention marks are valid in our territory.
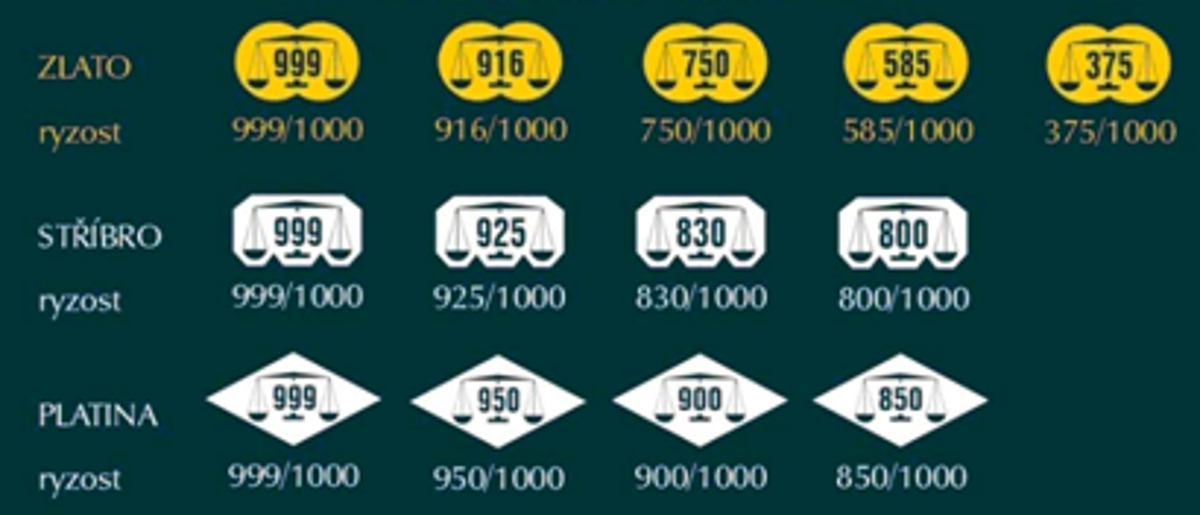

Czech conventional marks (marks of other members of the Convention are similar)
After the accession of the Czech Republic to the EU, the hallmarks of some member states of the union were also gradually recognized. Some countries, such as Germany, Italy and Austria, do not use hallmarks at all.
Production marks
In addition to hallmarks, there are also production marks. These are assigned by the manufacturer on the basis of the Punching Act and are stored in the register of the Assay Office. Marking with these marks is done by the manufacturer – he or she can only use them for products that he or she has made or assembled himself.
The Czech Mint uses three different production marks for different types of mintages.

mark for circulation coins and basic metal products (Nordic gold, brass, copper,…)

mark for products made of precious metals

mark for products within the issuance plan of the Czech Mint
The first mark, which takes the form of the letter "b" with a crown, refers to the oldest history of the Mint. The Czech Mint was founded on 1 July 1993 as an independent production division of the then joint-stock company Bižuterie, and its "b" remained with it even after it became independent.
The other two marks, which take the form of the letters "CM", are based on the logo of the Czech Mint, designed by academic sculptor Jiří Dostál.
 čeština
čeština
 slovenčina
slovenčina
 english
english
